Programming

Visual Prolog has its roots in Turbo Prolog, which was popularized by Borland in the mid 1980s. It is developed and supported by PDC A/S, Denmark. So how is Visual Prolog different from other Prolog implementations out there, for example, SWI-Prolog or Sicstus Prolog? Here are the key differences: 1) It is not an ISO Prolog […]

WH-Questions are questions that begin with the following words: – Who (“Who came here yesterday?”) – What (“What is the goal of this project?”) – When (“When can I visit my parents?”) – Where (“Where did he go?”) – Why (“Why is everyone running away?”) – Which (“Which is the book you recommend?”) – How […]

Eager Future2 is a Common Lisp library that facilitates parallel computation. It is based on the idea of a “future” that acts as a “proxy” for a concurrently computed expression. Unlike the “lparallel” library that I had discussed in the last article, this library does not give us control over the number of “worker threads” […]

You may recall that in the last article I had reviewed the book “Algorithms in Lisp” by Vsevolod Domkin. There was a reference to the lparallel library in Chapter 15 of the book. That immediately reminded me of the nice discussion of lparallel by Edi Weitz in Chapter 11 of his excellent book “Common Lisp Recipes”. Since […]
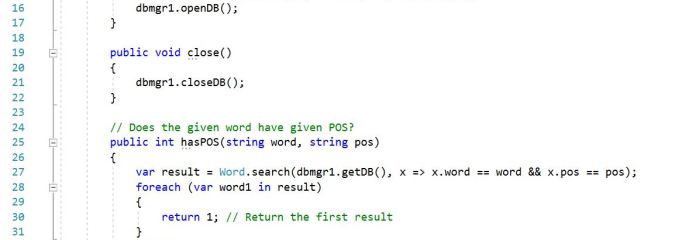
iLexicon is an “intelligent” dictionary that can be used to build Natural Language applications. I have two implementations, one in Lisp and another in Prolog. Both implementations are memory-based, in order to speed up performance. I have written several articles referencing it, for example see this. LiteDB is a NoSQL database for .NET. I […]

In the last article, I showed how we can invoke C# methods from LispWorks Enterprise Edition, through the COM/Automation interface. That approach relied on invoking the Automation methods dynamically, without depending on the Type library (*.tlb). In this article, I will discuss the other approach, which uses the Type library. According to LispWorks documentation, this […]

In an earlier article, I showed how to invoke C# methods from Sicstus Prolog. Today, I would like to detail the steps for doing the same from LispWorks Lisp. LispWorks Enterprise Edition comes budled with support for COM and Automation. This is what we will be using. What this means is that we have to […]

I have been looking around for a compact embedded NoSQL database library for .NET, to use as the back-end of my “iLexicon” system. “iLexicon” is written in Lisp and Prolog (I have written a few articles on it before). At present, the entire dictionary component (containing over 300,000 word entries) is resident in memory, and the […]

L-system is a powerful string rewriting system. Opusmodus supports an implementation of this system (inspired by and based on this implementation). It is possible to use the L-system to generate anything that can be described in terms of an alphabet and a set of rewriting rules. Let us start with a simple example: As you can see, there are […]
![C++20 [[nodiscard]] Attribute C++20 [[nodiscard]] Attribute](http://i0.wp.com/www.rangakrish.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/Example1-src.jpg?resize=675%2C240&ssl=1)
[[nodiscard]] attribute “encourages” the compiler to issue a warning when the return value from a function is ignored. It was introduced in C++ 17 and enhanced in C++ 20 to include a string literal that can be used as an explanation of the warning. Let us look at different cases one by one. Case-1: An enumeration […]
Recent Comments